The trend could force to modify planning of future generation projects; entrepreneurs and IDB study recommend solar and wind power production.

Eleven years ago, demand for electricity in the country grew by about 6% a year, but since 2010 it has been at an average rate of 3%. Tariff increases, technological improvements and a growing search for savings and efficiency affected consumption.
If this trend is followed, the National Electricity System (SEN) will require minimizing risk when planning generation projects; instead of large works could opt for gradual increases in the supply of energy, point several analyzes.
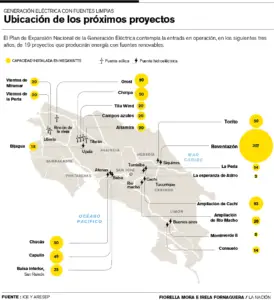
As of December 2015, the SEN had 3,068 Megawatts (MW) of installed generation capacity, according to data provided by ICE to the Public Services Regulatory Authority (Aresep).
However, Costa Rica does not use all this potential. In fact, in that year, December 15 was the day when the greatest use of generation capacity was recorded, but only 1,612 MW was used.
Of this installed capacity, only 0.03% were solar plants and 9% were wind power. The majority (75%) are hydroelectric plants that until 10 years ago seemed the best response to the growth of demand then.
However, consumption plummeted since 2007 and was even negative in 2009 due to the economic slowdown in the country resulting from the global crisis, according to the Expansion in Generation Plan 2018-2035 of the Costa Rican Electricity Institute (ICE).

While demand has increased in recent years, “depressed growth conditions are still persisting,” the ICE paper, released in May of this year, reveals.
Causes. The slowdown in the increase in energy consumption is the result of a combination of events that began after several increases in electricity rates from 2013, explained Luis Mesalles, an economist with the Central American Academy.
“The gains raised awareness and interest in saving the entire productive sector. They activated a permanent search for efficiency that took different routes,” said Mesalles.
Carlos Montenegro, deputy executive director of the Chamber of Industries of Costa Rica, predicts that the demand for energy will grow slowly for several more years unless the cost of light is lowered; an improbable scenario in his opinion.

“As more productive and residential sectors adjusted their consumption and replaced equipment with more thrifty technologies, demand growth fell and will grow slowly because of these changes in energy intensity.” This means that more subscribers were forced to raise their production without demanding more energy in the process, “Montenegro said.
The interest of businesses, companies, and factories to control their spending has led them to use their own generation facilities such as wind and solar plants and more efficient equipment, explained Erick Rojas, manager of the National Consortium of Electricity Companies of Costa Rica RL (Conelectricas RL), which integrates the electrification cooperatives Coopelesca RL, Coopesantos RL, Coopeguanacaste RL and Coopealfaroruiz RL
“Coopelesca, Coopeguanacaste, and Coopesantos have already done so and Coopealfaroruiz is in the process, this is just one example among several that, together, also reduce the demand”, added Montenegro.

The commitment to efficient technologies seems even to weigh more than the change in the productive structure of the country. According to data from the Central Bank, the service industry changed from 10% of production in 1966 to 40% in 2012, which cut off participation in agriculture and manufacturing.
Even one of the big electric consumers like Intel closed its manufacturing plant in Costa Rica to keep only the operation of financial and human services.
Energy with sun and wind. The slowdown in energy demand could also lead to rethinking the planning of future projects.

“It does not happen that we raise very large plants and then they are not used for less demand.” This is what happens to the ICE today with the Reventazón plant (in Siquirres). Some industries would opt for self-consumption, “said Erick Rojas.
Mesalles shares this impression in the case of the El Diquís hydroelectric plant; a project stranded for years and which ICE considers a priority. The hydro, which would have 650 megawatts of installed capacity, would be worth at least $ 3.694 million if it is built in Buenos Aires from Puntarenas.
“A plant like this could be left without much use, but its fixed costs of maintenance and depreciation, and those of other plants would continue to be distributed in the tariffs, now between fewer kilowatts consumed. consumers, it would accelerate the search for alternatives of own generation before more rises “, he affirmed.
Mario Alvarado, executive director of the Costa Rican Association of Energy Producers, believes that wind and solar plants would allow a more flexible and rapid response to the current growth rate of energy demand.
Alvarado recalled that a recent study by the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), which analyzed the conditions of the national electricity system, suggests that the authorities favor solar and wind-based plants, as they would function as risk management tools to ensure supply electric.
“It should be mentioned that wind and photovoltaic generation are modular generation systems, that is, generation capacity can be gradually increased and react to the development of demand in a much more flexible and faster way than if new hydroelectric power plants are installed”, says the IDB text.
The analysis even warns that while the Costa Rican power system can provide a large amount of rolling stock if necessary, “an arbitrarily high level of reserves will be unnecessarily costly.”
The rolling reserve refers to the generation scenario when certain plants operate at a lower intensity than their maximum capacity; it is so for safety reasons so that they are ready to respond to the supply in case of falls or other facilities or energy diversions.
According to the IDB’s analysis, efforts should focus on lower reserve requirements, including the development of better weather forecasting systems (for wind and wind) to consider these renewable sources in the rolling stock as well.
This issue is viewed with caution by ICE. Last May, Javier Orozco, director of Planning and Electrical Development at the Institute, told that the future development of the electricity system is expected to be mainly fueled by solar and wind power plants.
However, he insisted that investments should first be made in controllable sources, such as hydroelectric dams, that counteract the variability in the production of these other sources.
