A hernia is a sac formed by the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum). The sac passes through a hole or weak area in the strong layer of the abdominal wall surrounding the muscle, called the fascia. They can appear at any age from infancy to old age. The type of hernia depends on its location:
Femoral hernia.
It is a bump on the upper thigh, just below the groin. This type is more common in women than in men.
Hiatal hernia.
It occurs in the upper part of the stomach. A portion of the upper part of the stomach goes into the chest.
Surgical hernia.
Also known as eventration, it can occur through a scar if you have had abdominal surgery in the past.
Umbilical hernia.
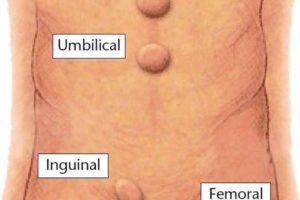
It is a bump around the navel. It happens when the muscle around the navel does not close completely after birth.
Inguinal hernia.
It is a lump in the groin. This type is more common in men. It can go down to the scrotum.
Main causes.
Usually, there is no clear cause for a hernia, but any activity or health problem that increases the pressure in the abdominal wall tissue and muscles can even lead to a hernia. Sometimes they can appear due to:

* Lifting heavy objects.
* Chronic constipation and push (strain) strongly to defecate.
* Perform any activity that raises the pressure inside the abdomen.
* Chronic cough or sneezing.
* Cystic fibrosis.
* Enlarged prostate, effort to urinate.
* Excess liquids in the abdomen (ascites).
* Peritoneal dialysis.
* Malnutrition.
* Smoking
* Testicle that has not descended.
* Soft tumor.
Effects of Hernia on the body.
Pain, which is greater when evagination is forming.
Intestinal transit disorder: difficulty in expelling gases and feces. The degree ranges from a simple tightening to total obstruction of intestinal transit.
They can be classified according to its:
–Etiology: Congenital or Acquired hernias
–Morphology: Slipped hernia: its contents (the meso or viscera) are part of the wall of the sac. –Location: Esophageal regato, Hiatus, Inguinal, Crural, Umbilical, Epigastric, Lumbar, Herniated disc, Brain herniation, Parastomal.
–Surgical treatment: Reducible or simple, Irreducible or incarcerated: cannot be reduced, which does not imply vascular compromise.
–Evolution: Uncomplicated, Complicated or strangulated hernia: it has vascular compromise, that is, it does not receive blood by compressing the vessels that supply it. Reducing a strangulated hernia is contraindicated.
–Contents of the hernia sac: Richter hernia: contains only part of the wall of the intestine, usually the antimesenteric edge. It is often strangled. Littre hernia: the one that contains a Meckel’s diverticulum Amyand hernia: the one that contains the cecal appendix with appendicitis or not.
Possible treatments.
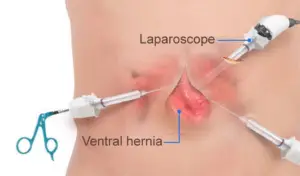
They consist of a surgical intervention to avoid complications and strangulation, followed by rehabilitation and medications indicated by the doctor. This is called Hernioplasty.

