Colposcopy is a diagnostic study performed by a specialist in gynecology in order to detect cancerous or abnormal cells that may affect the patient. This procedure is performed with the help of an instrument called a “colposcope”, with which the doctor allows the doctor to review in an illuminated and magnified way the internal tissues that may present conditions (cervix, vagina, and vulva).
The purpose of colposcopy is to discover lesions called dysplasias, created by the Human Papillomavirus, which if not treated in time, can become Cervical Cancer in the long run. According to Adrián Castro, gynecologist and obstetrician at Hospital Metropolitano, colposcopy is a diagnostic tool which helps define the severity of injuries. “By means of the evaluations that are carried out in a colposcopy, we can define if a dysplasia is mild or severe, its extension, if they involve the cervix or other parts, as well as follow up patients diagnosed with high-risk HPV”.
One of the indications to perform a colposcopy is that, if in the initial screening test known as the Papanicolau, the results are altered. This procedure should be performed in order to find the alteration in the previous tests. It will also be performed on patients with post-coital bleeding and those with lesions in another site of the lower genital tract.
Dr. Castro explains that the main difference from the Pap smear is that the Pap smear is used to detect abnormal changes in the cells of the cervix and must be performed periodically, while the colposcopy is an exam to take a closer look at the cervix and determine if there are precancerous cells. Therefore, this procedure is deeper and allows a better understanding of the state of health of this area.
To perform a colposcopy, no prior procedure is necessary. However, it should be noted that the patient must be out of her menstruation period since this can hide injuries, preventing it from being carried out correctly. Likewise, it is preferable not to have had sexual intercourse 24 hours before the medical appointment, not to use tampons, vaginal rings or menstrual cups.
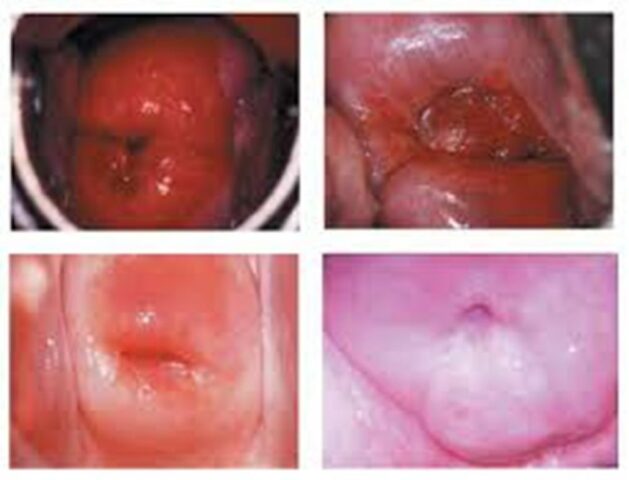
What happens during a colposcopy?
The consultation follows the normal guidelines of a medical appointment: the patient lies down in a gynecological position on the table and with the help of a speculum, which is used during vaginal examinations, and a camera called a colposcope, the doctor proceeds to review the lesion detection area. Subsequently, he proceeds to apply some substances such as physiological serums, acetic and iodinated solutions directly to the cervix to carry out a more in-depth observation.
This procedure is painless, however the patient may feel discomfort when the biopsy is performed, which usually feels like a small pinch. The test usually takes about half an hour and no specific aftercare is required.
The results of this exam are immediate “The patient will be able to know if she has a normal cervix, if she has low or high grade lesions, as well as a colposcopic impression by the gynecologist”, explained the specialist.

