If you are like most women, surely you are more interested in how your breasts look on the outside than in all that is under the skin. Familiarize yourself with them by self-examining and know how they work. This way you can protect them better.
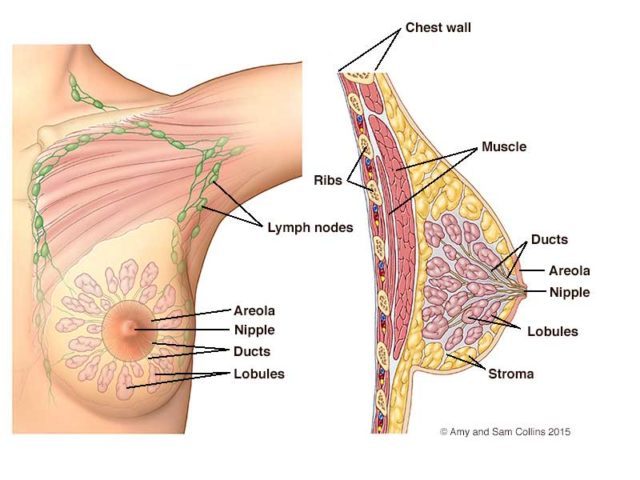
Areola. It is that round fine skin, pink or brown that surrounds the nipple. The areola contains hair follicles, sebaceous and sweat glands.
Nipple (round or cone-shaped). They are surrounded by supra-sensory muscle fibers and respond to sexual stimulation and coldness.
Connective tissue. Breasts are supported by connective tissues, composed mostly of collagen. The tissue forms superior ligaments, which support the breasts.
Pectoral muscles. Pectorals are between the back of the breasts and the rib cage.
Milk ducts. The glandular tissues form a system, each of which has a duct that guarantees the passage of milk to the nipple.
Fat. The size and shape of your breasts are primarily determined by the fat they contain, which protects the glands. Along with age, the amount of fat increases so the breasts lose firmness and fall downward.
Recommended habits for healthier breasts:
Limit alcohol
Women who usually drink more than one cup of alcohol a day have a higher risk of developing breast cancer. The theory of some scientists is that drinking damages the liver, which breaks down estrogen.
If the liver does not metabolize this hormone properly, the level of estrogen in the body will be higher. And along with that, the risk of developing the disease is increased.
Eat carrots
Women who develop breast cancer had lower levels of carotenoids (the pigment present in carrots and dark green leafy vegetables) than those who remain free of the disease.
Prefer olive oil
Consuming monounsaturated fats (present in olive and canola oils), instead of polyunsaturated fats, leads to a lower risk of cancer.
Sweat
Women -aged 40 or less- who exercise an average of 3 to 8 hours per week substantially reduced their breast cancer risk by 42%, compared to those who remain inactive.
Take the pill
Oral contraceptives not only relieve menstrual pain but also decrease inflammation and excessive sensitivity of the breasts related to menstruation, by eliminating the extreme hormonal fluctuations it causes.
Consume a daily dose of soy
Women who consume phytoestrogens, a compound similar to estrogen that is present in soy foods, have a lower incidence of breast cancer. They are believed to be beneficial because they help block the body’s natural estrogen, which promotes the growth of cancer cells in the breast, preventing them from entering the breast tissue.

Wear a bra, especially when exercising
The breasts are supported by weak ligaments, which can be easily stretched. Any intense or repetitive movement such as jumping or jogging distends and relaxes those tendons and therefore weakens and loosens the breasts no matter how small they are.
Maintain an ideal weight
Ask your doctor what your ideal weight is and in this way determine if you should lose a few pounds. The more you weigh, the more estrogen your body produces, and the higher the amount of estrogen, the greater the risk of breast cancer. If you need to lose weight your doctor can suggest a healthy eating plan and an exercise regimen that will help accelerate the process.

Lumps in the breasts
So you have discovered a small lump in the breast! And now what? First of all, calm down. Almost 80% of breast nodules are harmless. If you notice a bloody discharge coming from your nipple, but you do not feel any lumps, you may have a wart-like papilloma that sometimes forms in the milk ducts.
How to make a perfect self-exam
It is important that you become familiar with the way you self-exam your breasts, this way it is easier for you to detect any alteration. So take your health into your hands and follow our perfect self-examination advice.
You can start doing it a week after your period when the breasts are not sore or swollen. Start by lying on the bed, with a pillow under the right shoulder, your right hand under your head and using the fingertips of the first 3 fingers of your left hand, considering the index finger your number one, press the breast firmly, moving your hand in vertical direction throughout the breast. Repeat the same procedure in the other breast.
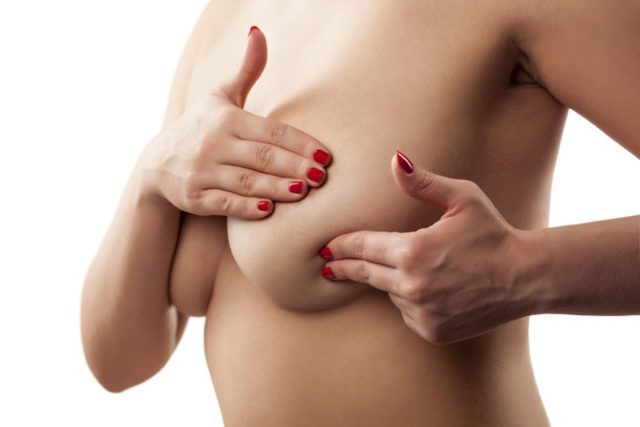
Also, you can check both breasts with soapy hands standing in the shower. Look carefully in the mirror and look for changes like redness and swelling of the nipples, if this is so, get a thorough medical examination.

