Menstruation is a natural process by which all women must pass. There are many myths about it but, actually, there is nothing strange in the matter. Some doubts should be clarified with an expert gynecologist who will guide you in order to thread a broader picture of the myths and realities in terms of menstruation.

What age is the first menstruation at?
The typical age of menarche -the first menstruation- has to be between 12 and 13 years old, and that has not changed much in the last 50 years. In some regions, the menarche has varied due to extreme nutritional conditions, wars, place of residence, city or countryside, province, etc.
In 8 out of 10 adolescents, menstruation lasts between 2 to 7 days and 30 milliliters of blood per cycle are lost. If a teenager loses more than 80 milliliters, it can cause anemia, a decrease in iron reserves, fatigue, lack of concentration, and motivation.
How is menstruation in adolescents? Is there any difference with the adult woman?
Certainly, there are differences. Most menstrual cycles in women happen every 28 to 30 days, lasting from 3 to 5 days. In adolescents, it may appear between 21 to 45 days without indicating, in most cases, an abnormal pattern. This happens until menstrual regularity is established. In this way, it can be said that adolescents start irregular menstrual cycles that will become regular over time.
However, in order to differentiate normal from abnormal menstrual variability, factors such as the weight of the patient, distribution and amount of hair, the presence of acne, sexual development, the appearance of the ovaries, and some alterations in the skin must be considered.
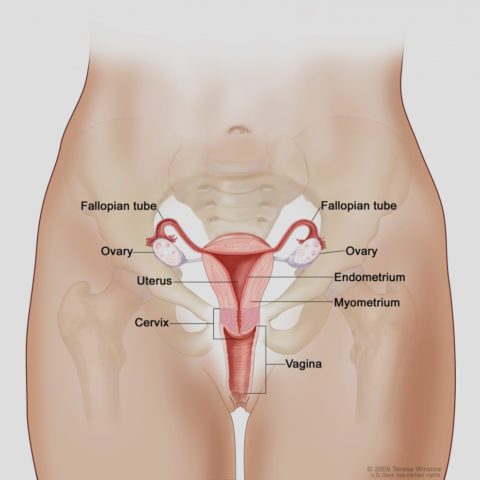
When you have any of these alterations; what happens?
5% of adolescents regulate their cycle every 14 to 20 days; 30% every 21 to 27 days; and 15% can last up to 35 to 41 days and 5% last over 42 days. These types of periods can last up to 6 years.
In general, short cycles that last less than 20 days or longer than 35 days, require a medical evaluation. Although you should know that in most adolescents, cycles are regularized around the 6th year post-menarche, which occurs around age 19.
Why are there short or long cycles?
Most doctors point out that the most frequent causes are the lack of ovulation, called anovulation, which normally occurs when a woman becomes pregnant. Other causes of lack of menstrual cycles, every 35 or more days called oligo-menorrhea can be a warning that something is not right and that you must urgently visit the gynecologist.
Which of these procedures should be taken more into account?
By far, the most common shortcomings of oligomenorrhea (menstrual disturbances) are hyperandrogenism, which means a level of increased androgen -a male hormone that causes increased hair in non-classical sites, such as, face, abdomen, back, pubis, thighs, legs, and acne.
The other cause that we must not forget is the so-called polycystic ovarian syndrome which means glandular alterations such as hyperandrogenism, abnormal resistance to insulin, and obesity. All this accompanied by the formation of more than 10 follicles of very small cysts in the ovary.
Are these procedures detected with the naked eye?
Well, yes and no. For example, hirsutism (increased hair) on the face is easily visible. However, it is necessary for the doctor to perform a more complete exploration of the adolescent in other cases.
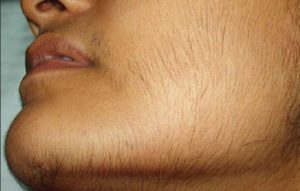
Is it important to be attentive for detections of abnormalities?
Absolutely, yes. Early detection of hyperandrogenism or polycystic ovary allows control of the problem. If these are not handled properly, the increase in initially thin hair becomes thick; besides that, the problem worsens if on your own you start using depilatory creams, waxes, epilators, electrolysis or some other product.
What should girls who have never menstruated in normal conditions do?
This procedure is called amenorrhea. It is designated primary if you have never menstruated, or secondary, if menstruation was previously presented.
A careful physical assessment must be applied to these girls. An evaluation of dietary habits for ruling out bulimia or anorexia and the frequency with which they exercise is very important since amenorrhea is common in athletes or ballet dancers.
Finally, it is convenient to review your clinical history, since a small percentage of girls have alterations in their chromosomes.
