In pediatric medicine, experts in growth and development say that our immune system is in charge of differentiating between our own and that of others to develop a response aimed at defending the organism from external agents.
Its response is specific since by forming antibodies against “the invaders”, it also can preserve in its memory, the memory of the first contact, and defend ourselves from subsequent attacks by the same germ.
Current vaccines are made from various types of antigens, being they the substances of infectious agents, capable of interacting with the cells of the immune system to sensitize it and produce antibodies.
There are vaccines made with toxoids, with subunits of protein particles, by genetic engineering, with attenuated live or dead microorganisms. All current research leads to creating vaccines that are more effective, safer, more protective, durable, easy to apply, and with lower costs. Thus reducing vaccine-preventable diseases.
There are vaccines made with toxoids, with subunits of protein particles, by genetic engineering, with attenuated live or dead microorganisms. All current research leads to creating vaccines that are more effective, safer, more protective, durable, easy to apply, and with lower costs. Thus reducing vaccine-preventable diseases.
Vaccination campaigns and scheduled vaccination systems, should always fully comply with the “cold chain” that corresponds to the complex system of preservation, transport, and handling techniques for these drugs and any biological product to guarantee their immunogenicity and maintain its effectiveness.
Some people wonder if it is better to acquire defenses by the disease rather than by vaccines, the answer is “No ” because some of these diseases can be fatal such as Tetanus, or leave sequelae such as Polio. Also, vaccines provide us with equal protection without taking serious risks from the disease.
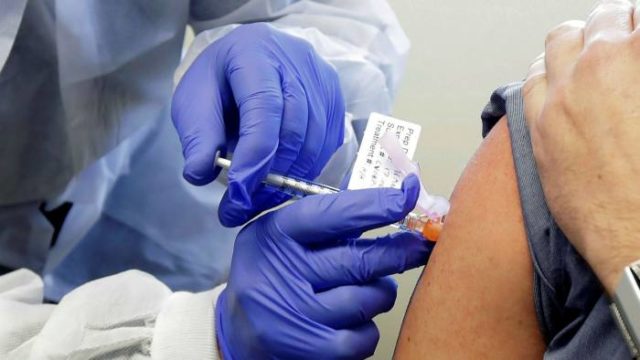
Careful handling of all protocols for application
Situations for which vaccines are contraindicated should be taken into account, being general contraindications; life-threatening allergic or anaphylactic reactions, seizures in the immediate period after application, active immunosuppressive diseases, or patients receiving treatment with steroids, chemotherapies, and/or radiotherapies.
Each vaccine has its specifications for contraindications, which must be reviewed before its application, so the child’s representatives should be questioned, before vaccination, in search of any antecedent that shows a certain severity.
Several vaccines can be applied on the same day but not mixed, although there are some such as yellow fever that must be applied at least 3 weeks apart to others.
The parts of the body where vaccines are placed in children under 18 months are applied to the lateral aspect of the thigh in the middle third; this site corresponds to the vast lateral. In older than 18 months; that is, a year and a half, it is applied to the deltoid muscle in the arm.
Types
The BCG is the first vaccine given the day after the baby is born; it is to prevent serious forms of tuberculosis, applied to the right arm. Live attenuated poliomyelitis is applied as drops to the mouth. If the vaccination schedule is interrupted, it is not necessary to start again, it must be restarted was interrupted to complete the missing doses.
Advice for mothers
Women who are already mothers must remember how important it is for the life of their baby to fully comply with the vaccination scheme as a vital component for the life of the baby, this does not mean that he will not get sick, but you are ensuring that his body will have strong defense mechanisms against diseases that may occur during his lifetime.

